Evaluate the effectiveness of fiscal policy in achieving economic growth
Evaluate the effectiveness of fiscal policy in achieving economic growth. (15m)
ANS:
Economic growth refers to an increase in the output of an economy, as measured by increase in real GDP. Economic growth comprises of consumption spending, investment spending, govt spending and net exports. Typically, the govt aims to achieve high economic growth in each period. This essay will evaluate the effectiveness of fiscal policy the govt implements to achieve its economic growth objectives.
(Body – explain how policy works)
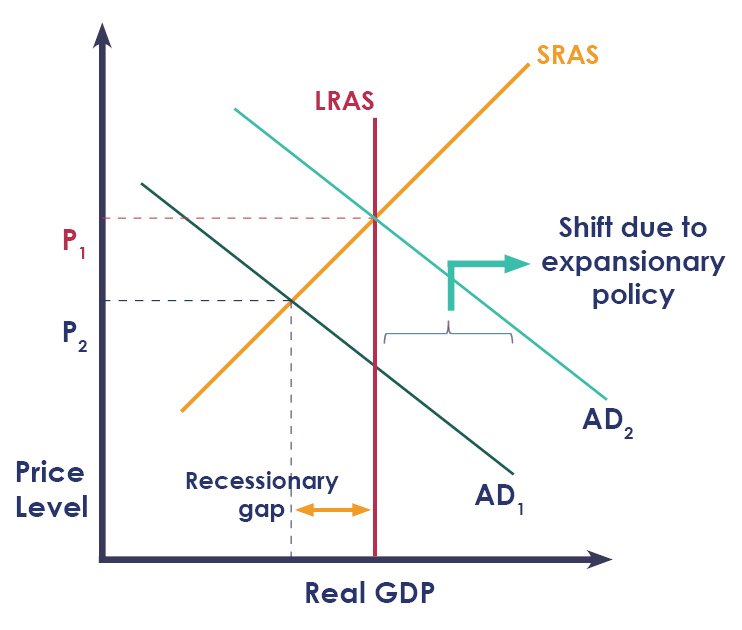
To boost the level of economic growth, the govt may implement expansionary fiscal policy. This refers to the manipulation of govt spending and taxes to increase the level of economic activity. For instance, SG govt spent 100 billion SGD in 2020 to boost the economy, after it suffered due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This boosted govt spending, causing AD to rise, and the AD curve to shift rightwards.
The govt may also reduce corporate income tax or personal income tax rates. If so, after tax profits for firms and disposable income for consumers will rise respectively; this allows them to spend more on capital goods and consumption goods. Investment spending and consumption spending may then rise, causing AD to rise.
State trigger, 2. Explain trigger, 3. State which component of AD changed, if applicable, 4. State AD or AS change, 5. State diagram change)
With the initial increase in AD from the higher govt spending, there is an initial increase in real GDP. National income level is boosted, and households have a higher disposable income. For every additional dollar of income they earn, they will spend a fraction of it on goods and services. This is referred to as the marginal propensity to consume (mpc). The larger the mpc is, the more consumers will spend on goods and services from their additional dollar of income. This causes AD to increase even more, leading to a further increase in real GDP. As such, there is a multiplier effect that occurs, causing the overall increase in real GDP to be higher than that of the initial increase in govt spending.
(Body – effective)
Fiscal policy may be effective in achieving higher economic growth as govt spending, if used as a tool, can directly increase AD. In addition, the govt may vary the spending amount on specific sectors, so that the economy can be more effectively supported. For instance, in 2020, the SG govt provided higher wage subsidies for sectors such as F&B and frontline services, as they had to cease operations during the lockdown period. This prevented the sectors from closing down and allowed them to recover later on when the economy re-opened, supporting economic growth.
(Body – not effective)
However, fiscal policy may not be completely effective at achieving higher economic growth. This may be due to a small multiplier effect. As the above explained, a small multiplier size is due to a small MPC value. Households may spend a limited fraction of their next dollar of income, causing the subsequent increase in AD from consumption spending to be limited. This would limit the increase in real GDP. For instance, during recessionary periods, such as in 2020 in SG, when COVID-19 devastated the economy, consumer confidence fell. Consumers grew more cautious, and decided to save more, which then reduced the size of the MPC. Thus, the govt had to increase their govt spending, or else fail to achieve their targeted economic growth rates.
Expansionary fiscal policies may also incur an opportunity cost. Opp cost refers to the benefit / value of the next best alternative forgone when a choice is made. If the govt spends more on a specific sector, it may have less resources to do so for other sectors; or, as in the case of SG, with the govt spending from its past reserves, it would have less to spend in the future if a similar crisis were to strike. This would reduce the ability of the govt to implement a similar policy in the future, thus impacting on future economic growth.
(Evaluation)
In conclusion, fiscal policy may still be the most effective policy the govt can implement to achieve higher economic growth. Monetary policy, used by the central bank to influence the economy, may be complementary to fiscal, owing to its limited range of tools that can be deployed. Fiscal policies, on the other hand, can be targeted to specific sectors of the economy, providing assistance to where it is needed. To mitigate the limitations of the policy, the govt may also implement other policies. For instance, as the economy recovers from a crisis after a period of expansionary fiscal policy, the govt may then raise taxes to improve the budget balance again.
(other economic growth goals: sustainable growth, sustained growth, inclusive growth)
sustainable: conserving resources (eg. don’t overuse)
sustained: real GDP consistently increases
inclusive: minimal worsening of income inequality issues
Need more help in understanding Economics?
Join Afterskool’s Economics tuition classes for tips and tricks to master the subject.
Click here to enrol.